Arduino Tutorial Capacitive Touch Sensors 21 Steps with Pictures Circuit Diagram
BlogArduino Tutorial Capacitive Touch Sensors 21 Steps with Pictures Circuit Diagram NodeMCU-Based IoT Project: Connecting Touch Sensor The goal of this tutorial is to enable you to capture and send data to cloud from NodeMCU. Networking: Combine touch input with the ESP32's Wi-Fi capabilities to send data to a server or control IoT devices remotely. Multiple Sensors: Integrate multiple touch sensors for more complex applications, such as touch-sensitive keyboards. A capacitive touch sensor, also known as a touch button or touch switch, is a commonly used device to control other gadgets, such as a touchable lamp. It performs the same function as a button, but is often chosen over a button for modern devices in order to give them a more polished appearance. The Touch Sensor Pinout The touch sensor has

A capacitive touch sensor, also known as a touch button or touch switch, is frequently used to operate devices (e.g. a touchable lamp). It has the same purpose as a button. Finally, we'll answer your questions in our live Q and A. Why should I use capacitive touch sensors? - 2:46 How does a capacitive touchscreen work? How does a touch sensor work? - 8:34 How to build a basic capacitive touch sensor? - 10:20 What is a gerber file? - 11:54 Is mTouch still used? What is mTouch? In this tutorial, I will show how to use an Arduino for touch and capacitive sensing. Not just touch, but to detect the force exerted and the distance from the finger too. I will briefly explain the theory and then build a touch sensitive circuit with a simple wire, resistor and LED along with the Arduino. Let's get started!
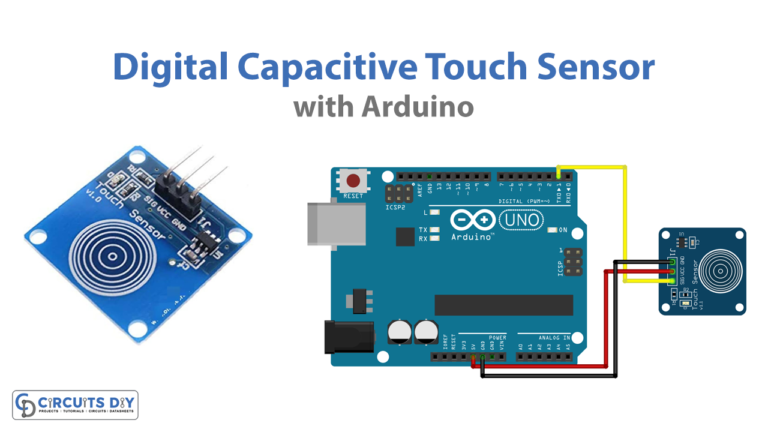
Arduino capacitive touch sensing tutorial Circuit Diagram
In this blog post I talk about how you can use the TTP223B Capacitive Touch sensor with a WeMos D1 Mini (ESP8266) using the Arduino IDE.
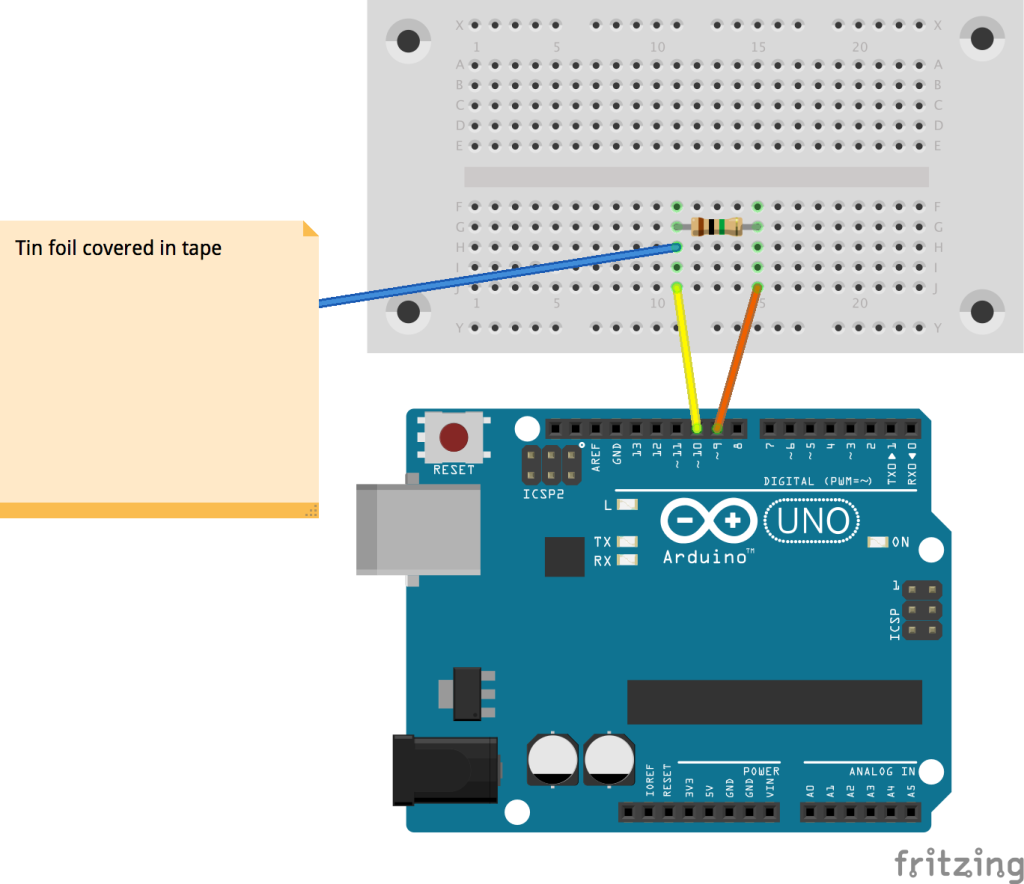
Touch sensor has been common nowadays for displays and IoT projects with Arduino. They can be found in lamps, touch screens of smartphones, and other wide arrays of applications as well. However, do you understand the working principle of a touch sensor and how to use it alongside your Arduino?
