Solved 1 Design a step up transformer that would take an Circuit Diagram
BlogSolved 1 Design a step up transformer that would take an Circuit Diagram A transformer designed to reduce the voltage from primary to secondary is called a step-down transformer. The transformation ratio of a transformer will be equal to the square root of its primary to secondary inductance (L) ratio. RELATED WORKSHEETS: Step-up, Step-down, and Isolation Transformers Worksheet In this electronics 101 series episode, I get into what step up and step down transformers are, how they work (electromagnetic induction), what we humans us

A boost converter (step-up converter) is a DC-to-DC power converter that steps up voltage (while stepping down current) from its input (supply) to its output (load). It is a class of switched-mode power supply (SMPS) containing at least two semiconductors (a diode and a transistor) and at least one energy storage element: a capacitor, inductor Key learnings: Step Up Transformer Definition: A step-up transformer is a device that increases the voltage while decreasing the current from its primary to its secondary side.; Working Principle: It operates by converting electrical energy to magnetic energy and back, utilizing the transformer core.; Voltage Transformation Formula: The formula for output voltage in a step-up transformer shows

Circuit Diagram, Working and Formula ...
Figure 1: step up transformer wiring diagram . What does a Step-up Transformer Do. Step-up transformers are used in electronic devices like inverters, batteries, and stabilizers to balance low and higher voltages in transformers. They are used in power transmission, playing a crucial role in transferring power to locations far from generating
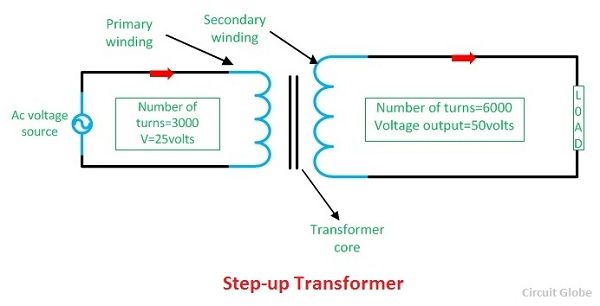
Step-down transformer: (many turns :few turns). The step-up/step-down effect of coil turn ratios in a transformer (Figure above) is analogous to gear tooth ratios in mechanical gear systems, transforming values of speed and torque in much the same way: (Figure below) Torque reducing gear train steps torque down, while stepping speed up. The step-up transformer gives the higher voltage as a output because the voltage is directly proportional to the number of turns in the windings. Hence, in a step up transformer with N 1 turns in primary winding, It increases or steps up the voltage in the output circuit. It decreases or steps down voltage in the output circuit. Effect on Schematic diagram of the transformer. A schematic diagram of a step-up transformer is shown in image 2, wi th T 1 and T 2 representing the turns of the primary and secondary windings and V 1 and V 2 representing the in put and output voltages, respectively. The transformer's output winding is the secondary winding, whereas the primary winding is the transformer's input winding.
![[DIAGRAM] Electrical Step Up Transformer Diagram Circuit Diagram](https://s3mn.mnimgs.com/img/shared/ck-files/ck_58429ec8071f1.jpg)